WHAT IS UNKNOWN ABOUT POLYURETHANE AND POLYUREA?
WHAT IS UNKNOWN ABOUT POLYURETHANE AND POLYUREA?
What are Polyurethane and Polyurea?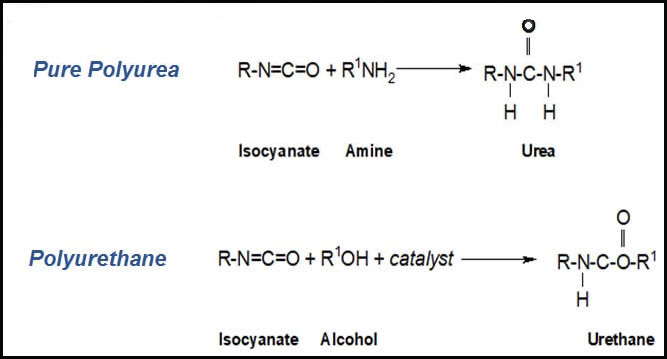
Polyurethane is a repeating sequence of monomers containing hydrogen, carbon, nitrogen and oxygen that are linked together by the polymerization process to form a polymer. The polymer is then introduced into an alcohol catalyst containing hydroxyls and isocyanates to become a polyisocyanate called polyurethane as a result of an exothermic reaction.
This reaction often leads to the use of the final product.
Polyurea is an elastomer discovered in the 1980s, formed by an additional catalyst reaction that occurs as the product is applied.
Therefore, it can produce an exothermic reaction on the substrate while curing.
In this case, unlike many polyurethanes used in industry, the application
process, the final product is not formed.
What are the characteristics of Polyurethane and Polyurea?
Polyurethane is a manufacturing chameleon and can be used to create a variety of rigid or elastic foams, coatings and materials depending on the additives and processes used. When used as a coating, polyurethane has a much longer cure time and without appropriate additives it can occasionally change color or become cloudy over time and does not exhibit the same level of durability and abrasion resistance as polyurea.
 Polyurea starts as an elastomer and, again depending on the additives and treatments used, can retain its elastomeric properties after application. This can give a polyurea system superior wear, corrosion and adhesion properties compared to other materials. Some formulations also exhibit excellent UV resistance without long-term discoloration.
Polyurea starts as an elastomer and, again depending on the additives and treatments used, can retain its elastomeric properties after application. This can give a polyurea system superior wear, corrosion and adhesion properties compared to other materials. Some formulations also exhibit excellent UV resistance without long-term discoloration.
What are the uses of Polyurethane and Polyurea?
Polyurethane is often used to make mattress foam, insulation and hardened protective coatings, polyurethane is one of the most popular polyols in modern industry. You can find it in shoes, housing, furniture, cars and more.
Polyurea's unique properties make it an ideal candidate for durable, beautiful coatings that withstand some of the harshest conditions, including marine and industrial environments. It remains transparent under UV light and manages humid environments, making it an attractive coating for other building surfaces such as floors and countertops.
What does the future hold for Polyurethane and Polyurea in the industry?
 With advances in raw materials, surface preparation methods and spray equipment, the failure rate of polyureas is decreasing and the use of polyureas is increasing. As the industry learns the "do's and don'ts" of choosing the right system and chemistry for the job, the world is now beginning to trust polyureas again.
With advances in raw materials, surface preparation methods and spray equipment, the failure rate of polyureas is decreasing and the use of polyureas is increasing. As the industry learns the "do's and don'ts" of choosing the right system and chemistry for the job, the world is now beginning to trust polyureas again.
The truth about polyurea is that when this fast curing chemistry is properly formulated, specified and distributed,
can add significant value to many industrial applications. Polyurea chemistry can help reduce unwanted reactions with the natural or man-made environment. It can provide a high value solution for many corrosion and waterproofing applications.
Polyurethane and polyurea coatings offer an excellent option for many applications. However, their cure time properties and the versatility of the application process in harsh environmental conditions make polyurea coatings a more cost-effective system than many other systems.

Polyurethane is a repeating sequence of monomers containing hydrogen, carbon, nitrogen and oxygen that are linked together by the polymerization process to form a polymer. The polymer is then introduced into an alcohol catalyst containing hydroxyls and isocyanates to become a polyisocyanate called polyurethane as a result of an exothermic reaction.
This reaction often leads to the use of the final product.
Polyurea is an elastomer discovered in the 1980s, formed by an additional catalyst reaction that occurs as the product is applied.
Therefore, it can produce an exothermic reaction on the substrate while curing.
In this case, unlike many polyurethanes used in industry, the application
process, the final product is not formed.
What are the characteristics of Polyurethane and Polyurea?
Polyurethane is a manufacturing chameleon and can be used to create a variety of rigid or elastic foams, coatings and materials depending on the additives and processes used. When used as a coating, polyurethane has a much longer cure time and without appropriate additives it can occasionally change color or become cloudy over time and does not exhibit the same level of durability and abrasion resistance as polyurea.
 Polyurea starts as an elastomer and, again depending on the additives and treatments used, can retain its elastomeric properties after application. This can give a polyurea system superior wear, corrosion and adhesion properties compared to other materials. Some formulations also exhibit excellent UV resistance without long-term discoloration.
Polyurea starts as an elastomer and, again depending on the additives and treatments used, can retain its elastomeric properties after application. This can give a polyurea system superior wear, corrosion and adhesion properties compared to other materials. Some formulations also exhibit excellent UV resistance without long-term discoloration.What are the uses of Polyurethane and Polyurea?
Polyurethane is often used to make mattress foam, insulation and hardened protective coatings, polyurethane is one of the most popular polyols in modern industry. You can find it in shoes, housing, furniture, cars and more.
Polyurea's unique properties make it an ideal candidate for durable, beautiful coatings that withstand some of the harshest conditions, including marine and industrial environments. It remains transparent under UV light and manages humid environments, making it an attractive coating for other building surfaces such as floors and countertops.
What does the future hold for Polyurethane and Polyurea in the industry?
 With advances in raw materials, surface preparation methods and spray equipment, the failure rate of polyureas is decreasing and the use of polyureas is increasing. As the industry learns the "do's and don'ts" of choosing the right system and chemistry for the job, the world is now beginning to trust polyureas again.
With advances in raw materials, surface preparation methods and spray equipment, the failure rate of polyureas is decreasing and the use of polyureas is increasing. As the industry learns the "do's and don'ts" of choosing the right system and chemistry for the job, the world is now beginning to trust polyureas again.The truth about polyurea is that when this fast curing chemistry is properly formulated, specified and distributed,
can add significant value to many industrial applications. Polyurea chemistry can help reduce unwanted reactions with the natural or man-made environment. It can provide a high value solution for many corrosion and waterproofing applications.
Polyurethane and polyurea coatings offer an excellent option for many applications. However, their cure time properties and the versatility of the application process in harsh environmental conditions make polyurea coatings a more cost-effective system than many other systems.